By Harlan Bengtson
Introduction to Partially Full Pipe Flow Calculations
If you want to obtain an Excel spreadsheet for partially full pipe flow calculations, click here to go to the download page. Read on for information about Excel spreadsheets that can be used as partially full pipe flow calculators.
The Manning equation can be used for flow in a pipe that is partially full, because the flow will be due to gravity rather than pressure. the Manning equation [Q = (1.49/n)A(R2/3)(S1/2) for (U.S. units) or Q = (1.0/n)A(R2/3)(S1/2) for (S.I. units)] applies if the flow is uniform flow For background on the Manning equation and open channel flow and the conditions for uniform flow, see the article, "Manning Equation/Open Channel Flow Calculations."
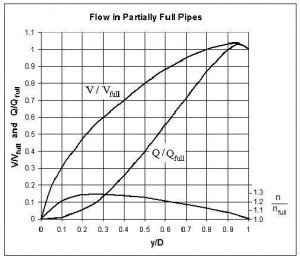
Direct use of the Manning equation as a partially full pipe flow calculator, isn't easy, however, because of the rather complicated set of equations for the area of flow and wetted perimeter for partially full pipe flow. There is no simple equation for hydraulic radius as a function of flow depth and pipe diameter. As a result graphs of Q/Qfull and V/Vfull vs y/D, like the one shown at the left are commonly used for partially full pipe flow calculations. The parameters, Q and V in this graph are flow rate an velocity at a flow depth of y in a pipe of diameter D. Qfull and Vfull can be conveniently calculated using the Manning equation, because the hydraulic radius for a circular pipe flowing full is simply D/4.
With the use of Excel formulas in an Excel spreadsheet, however, the rather inconvenient equations for area and wetted perimeter in partially full pipe flow become much easier to work with. The calculations are complicated a bit by the need to consider the Manning roughness coefficient to be variable with depth of flow as discussed in the next section.
Excel Spreadsheet/Partially Full Pipe Flow Calculator for Pipe Less than Half Full
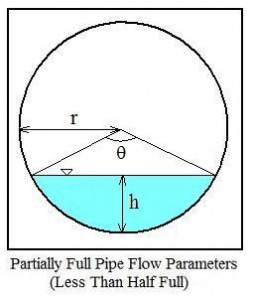
The parameters used in partially full pipe flow calculations with the pipe less than half full are shown in the diagram above. K is the circular segment area; S is the circular segment arc length; h is the circular segment height; r is the radius of the pipe; and θ is the central angle.
The equations below are those used, together with the Manning equation and Q = VA, in the partially full pipe flow calculator (Excel spreadsheet) for flow depth less than pipe radius, as shown below.
- h = y
- θ = 2 arccos[ (r - h)/r ]
- A = K = r2(θ - sinθ)/2
- P = S = rθ
The equations to calculate n/nfull, in terms of y/D for y < D/2 are as follows
- n/nfull = 1 + (y/D)(1/3) for 0 < y/D < 0.03
- n/nfull = 1.1 + (y/D - 0.03)(12/7) for 0.03 < y/D < 0.1
- n/nfull = 1.22 + (y/D - 0.1)(0.6) for 0.1 < y/D < 0.2
- n/nfull = 1.29 for 0.2 < y/D < 0.3
- n/nfull = 1.29 - (y/D - 0.3)(0.2) for 0.3 < y/D < 0.5
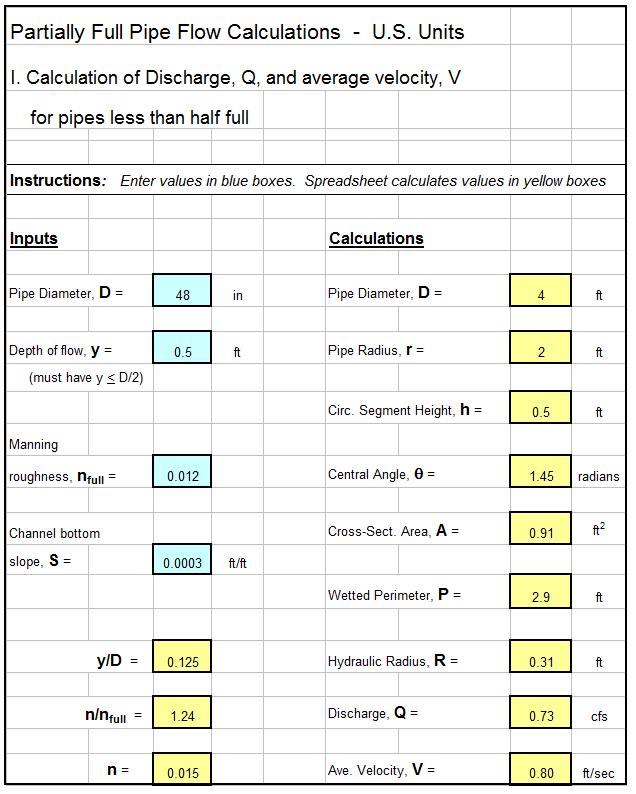
The Excel template shown below can be used as a partially full pipe flow calculator to calculate the pipe flow rate, Q, and velocity, V, for specified values of pipe diameter, D, flow depth, y, Manning roughness for full pipe flow, nfull; and bottom slope, S, for cases where the depth of flow is less than the pipe radius. This Excel spreadsheet and others for partially full pipe flow calculations are available in either U.S. or S.I. units at a very low cost from the download page.
Excel Spreadsheet/Partially Full Pipe Flow Calculator for Pipe More than Half Full
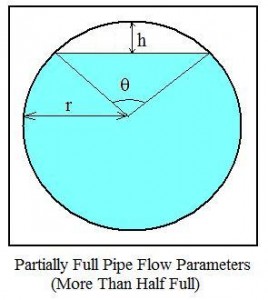 The parameters used in partially full pipe flow calculations with the pipe more than half full are shown in the diagram at the right. K is the circular segment area; S is the circular segment arc length; h is the circular segment height; r is the radius of the pipe; and θ is the central angle.
The parameters used in partially full pipe flow calculations with the pipe more than half full are shown in the diagram at the right. K is the circular segment area; S is the circular segment arc length; h is the circular segment height; r is the radius of the pipe; and θ is the central angle.
The equations below are those used, together with the Manning equation and Q = VA, in the partially full pipe flow calculator (Excel spreadsheet) for flow depth more than pipe radius, as shown below.
- h = 2r - y
- θ = 2 arccos[ (r - h)/r ]
- A = πr2 - K = πr2 - r2(θ - sinθ)/2
- P = 2πr - S = 2πr - rθ
The equation used for n/nfull for 0.5 < y//D < 1 is: n/nfull = 1.25 - [(y/D - 0.5)/2]
An Excel spreadsheet like the one shown above for less than half full flow, and others for partially full pipe flow calculations, are available in either U.S. or S.I. units at a very low cost from the downloads page.
References
1. Camp, T.R., "Design of Sewers to Facilitate Flow," Sewage Works Journal, 18 (3), 1946
2. Steel, E.W. & McGhee, T.J., Water Supply and Sewerage, 5th ed., New York, McGraw Hill Book Company, 1979
3. ASCE, 1969, Design and Construction of Sanitary and Storm Sewers, NY.
4. Bengtson, Harlan H., Uniform Open Channel Flow and The Manning Equation, an online, continuing education course for PDH credit.
5. Bengtson, H.H., "Partially Full Pipe Flow Calculations with Spreadsheets", an Amazon Kindle e-book.
6. Bengtson, H.H., "Partially Full Pipe Flow Calculations with Excel Spreadsheets", an online blog article.